Download Linux VirtualBox Images. List of VirtualBox Images. Kali Linux 2020.04: Download (4.1GB) PCLinuxOS 2020.10: Download (3.4GB) Mageia 7.1: Download (1.9GB). Want to download Kali Linux custom images? We have generated several Kali Linux VMware and VirtualBox images which we would like to share with the community. Note that the images provided below are maintained on a “best effort” basis.
- Kali Linux Iso Download
- Kali Linux Downloads
- Kali Linux Virtual
- Download Kali Linux Iso For Virtualbox
- Kali Linux Iso For Oracle Vm Virtualbox
- Kali Linux Iso Image For Virtualbox
Kali Linux is preinstalled with over 600 penetration-testing programs, including nmap (a port scanner), Wireshark (a packet analyzer), John the Ripper (a password cracker), Aircrack-ng (a software suite for penetration-testing wireless LANs), Burp suite and OWASP ZAP (both web application security scanners). Kali Linux can run natively when installed on a computer's hard disk, can be booted from a live CD or live USB, or it can run within a virtual machine. It is a supported platform of the Metasploit Project's Metasploit Framework, a tool for developing and executing security exploits.
It was developed by Mati Aharoni and Devon Kearns of Offensive Security through the rewrite of BackTrack, their previous forensics Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. The third core developer Raphaël Hertzog joined them as Debian expert.
Kali Linux is based on Debian Wheezy. Most packages Kali uses are imported from the Debian repositories.
Kali Linux is developed in a secure location with only a small number of trusted people that are allowed to commit packages, with each package being signed by the developer. Kali also has a custom built kernel tha is patched for injection. This was primarily added because the development team found they needed to do a lot of wireless assessments.
What's New:
- 0006393: [Kali Package Bug] 'Failed to execute default Terminal Emulator' INPUT/OUTPUT error (daniruiz)
- 006668: [Queued Tool Addition] dnscat2 (sbrun)
- 0006801: [Kali Package Bug] screenshot directory not found (daniruiz)
- 0006839: [General Bug] 2020.3 Netinstaller default installation appears to be broken (rhertzog)
- 0006537: [Queued Tool Addition] hostapd-mana (sbrun)
- 0004348: [Queued Tool Addition] CertGraph (sbrun)
- 0006621: [Queued Tool Addition] Whatmask (sbrun)
- 0006147: [Queued Tool Addition] apple_bleee - Apple BLE research (sbrun)
- 0006141: [Queued Tool Addition] goDoH - A DNS-over-HTTPS C2 (sbrun)
- 0006697: [Tool Upgrade] metasploit-framework 6.0.3 available (sbrun)
- 0002037: [Queued Tool Addition] proxychains-ng (fork of proxychains) (sbrun)
- 0006464: [Queued Tool Addition] FinalRecon - The Last Web Recon Tool You'll Need (g0tmi1k)
- 0006718: [General Bug] Cant't Change Kali Linux Terminal Font (daniruiz)
- 0006685: [General Bug] Qterminal unable to change font (daniruiz)
New Desktop Environment and GTK3 Theme
There are a ton of updates to go over for this release, but the most in your face item that everyone is going to notice first are the changes to the desktop environment and theme. So let’s cover that first.
An update to the desktop environment has been a long time coming. We have been talking about how to address this, what we wanted to do, experimenting on different approaches, and so on for months now. As a summary we had a few issues we wanted to address head-on:
- Performance issues – Gnome is a fully-featured desktop environment with a ton of awesome things it can do. But all these features comes with overhead, often overhead that is not useful for a distribution like Kali. We wanted to speed things up, and have a desktop environment that does only what it’s needed for, and nothing else. Gnome has been overkill for most Kali users, as many just want a window manager that allows you to run multiple terminal windows at once, and a web browser.
- Fractured user experience – We support a range of hardware, from the very high end to the very low. Because of this, traditionally our lower-end ARM builds have had a completely different UI than our standard. That’s not optimal, and we wanted to unify this experience so it did not matter if you were running on a bare metal install on a high end laptop or using a Raspberry Pi, the UI should be the same.
- Modern look – We have been using the same UI for quite a while now, and our old theme maintainer had moved on due to lack of time. So we wanted to go with something fresh, new, and modern.
To help us address these items, we tracked down Daniel Ruiz de Alegría and started the development of a new theme running on Xfce. Why Xfce? After reviewing the above issues, we felt that Xfce addressed them best while still being accessible to the majority of users.
The solution we’ve committed to is lightweight and can run on all levels of Kali installs. It is functional in that it handles the various needs of the average user with no changes. It is approachable where it uses standard UI concepts we are all familiar with to ensure there is no learning curve. And it looks great with modern UI elements that make efficient use of screen space.
We are really excited about this UI update, and we think you are going to love it. However, as UI can be a bit like religion, if you don’t want to leave Gnome don’t worry. We still have a Gnome build for you, with a few changes already in place. As time goes by, we will be making changes to all of the desktop environments we release installs to get them “close” to a similar user experience no matter what DE you run. There will be limits to this, as we don’t have the resources to heavily invest in tweaking all these different environments. So if there is something you would like to see, feel free to submit a feature request!
We have also released a FAQ about the new theme that you can find on our docs page. This includes some common items like how to switch to the theme on your existing install, how to change off of it if you don’t like it, and so on.
Kali Undercover
With the change to the environment, we thought we would take a side step and do something fun. Thanks to Robert, who leads our penetration testing team, for suggesting a Kali theme that looks like Windows to the casual view, we have created the Kali Undercover theme.
Say you are working in a public place, hacking away, and you might not want the distinctive Kali dragon for everyone to see and wonder what it is you are doing. So, we made a little script that will change your Kali theme to look like a default Windows installation. That way, you can work a bit more incognito. After you are done and in a more private place, run the script again and you switch back to your Kali theme. Like magic!
Kali-Docs is now on Markdown and new home (/docs/)
This may not be as flashy as the new theme, but the changes to the docs we have done is just as significant.
One of our go-forward goals with Kali is to move more of the development into the public and make it as easy as possible for anyone (that means you!) to get involved and contribute to Kali. That’s what our move to GitLab earlier in the year was all about. Another part of this is changing how we deal with docs.
We have since moved all of our documentation into Markdown in a public Git repository. From here on out anyone, not just Kali staff, can contribute to better documentation through merge requests. We will still approve any content changes, but once merged, changes will be automatically available on the docs section of our website.
We encourage everyone to get involved! If you see something wrong in the existing docs, change it! If you have an idea for new docs, write it! These sorts of contributions make Kali better for everyone.
This is just the first step. With this change in place, coming soon watch for a kali-docs package in Kali that gives you full offline access to the documentation on every install of Kali. Perfect for those situations where you are working in a closed-off environment with no Internet access.
Public Packaging
One of the more significant new documents we have done is documenting how you can make a new package that will get included in Kali.
One of the most common bug reports is requests for us to add new tools or update existing ones. Oftentimes, by the tool developers themselves as they recognize that having their tool in the Kali repo is the easiest distribution channel for security assessment tools there is. The volume of this has always been difficult to keep up with, and we have to make some hard decisions on where to commit our limited resources.
Now with this work-flow in place and documented, you don’t have to wait on us. Go ahead and package up your tool and submit it off to us for approval. This is an awesome way to get involved with improving Kali.
BTRFS during setup
Another significant new addition to the documentation is the use of BTRFS as your root file system. This is an amazing approach documented by Re4son, that when done gives you the ability to do file system rollbacks after upgrades.
When you are in a VM and about to try something new, you will often take a snapshot in case things go wrong you can easily go back to a known-good state. However, when you run Kali bare metal that’s not so easy. So you end up being extra careful, or if things go wrong have a lot of manual clean up to do. With BTRFS, you have this same snapshot capability on a bare metal install!
As this is new, it’s not integrated into our installer yet. Once we get some feedback on how it’s working for everyone, the next step is to streamline this and make it an easier option in our installer. So if you try it out, be sure to let us know how it works for you!
PowerShell
On to other features, in case you missed it PowerShell is now in Kali (We have a blog post about it). This has been really great to bring the ability to execute PowerShell scripts directly on Kali.
NetHunter Kex – Full Kali Desktop on Android phones
Another feature we are super excited about is the introduction of NetHunter Kex. In a nutshell, this allows you to attach your Android device to an HDMI output along with Bluetooth keyboard and mouse and get a full, no compromise, Kali desktop. Yes. From your phone.
We had a live Penetration Testing with Kali course we were teaching, and NetHunter Kex was just in a beta stage. So we wanted to really push the limits. So, in the live course, what we did was attach a USB-C hub to our OnePlus7. This gave us HDMI and Ethernet access. We attached the HDMI to the projector and used a bluetooth keyboard/mouse. With this, we were able to do an entire PWK module from the phone.
This is a feature you have to see to believe. Until you experience it, you won’t fully understand what this provides. With a strong enough phone, this is very similar to using a nice full-featured portable ARM desktop that happens to fit in your pocket. The possible ways you can leverage this in assessments is huge.
To get a full breakdown on how to use NetHunter Kex, check out our docs at.
ARM
2019.4 is the last release that will support 8GB sdcards on ARM. Starting in 2020.1, a 16GB sdcard will be the minimum we support. You will always be able to create your own image that supports smaller cards if you desire.
Kali Linux Iso Download
- RaspberryPi kernel was updated to 4.19.81, and the firmware package was updated to include the eeprom updates for the RaspberryPi 4.
During the release testing, a limited number of devices were not showing the Kali menu properly. This was not critical enough to delay the release, so instead as a work-around you can run the following command to display the menu correctly: apt update && apt dist-upgrade
Once this completes, log out, so you’re back at the login manager. Then switch to a console via CTRL+ALT+F11 (on the Chromebooks this is the key pointing left next to the ESC key).
Login and then run: rm -rf .cache/ .config/ .local/ && sync && reboot
After reboot, the menu will have the correct entries. We’re still looking into why it occurs on only some of the images.
Kali 2019.3 Release Notes
We are pleased to announce that our third release of 2019, Kali Linux 2019.3, is available immediately for download. This release brings our kernel up to version 5.2.9, and includes various new features across the board with NetHunter, ARM and packages (plus the normal bugs fixes and updates).
As promised in our roadmap blog post, there are both user facing and backend updates.
NetHunter Updates
The NetHunter crew has been adding in features left, right, and center to their project. One thing to note is package management is done through the F-Droid compatible NetHunter store, so you can even choose to have a NetHunter device without any Google Play.
The proxmark3 client supports RDV4 out of the box and NetHunter now also works with Android’s new partition layouts (A/B partitions no longer have one boot partition and one recovery partition. They are all the same, but twice! A few paths have also changed, such as /system now actually being under /system/system), which allows it to be built for the latest generation of devices.
Plus, there are new apps in the NetHunter app store, thanks to @mayank_metha for Rucky and the Termux team for Termux.
There are 4 additional images for you to try NetHunter on (some may look familiar, as they are back due to community demand):
- LG V20 International Edition
- Nexus 5X
- Nexus 10
- OnePlus 7 (Our new flagship device!)
With this announcement, the OnePlus 7 is now the phone we recommend for Kali NetHunter. It is the latest and greatest flagship device for half the price of other devices. The specifications are as follows:
- Snapdragon 855
- 8GB RAM
- 256GB storage
- Still cheaper than Google pixel 3a (mid-range phone!) ;)
And here is a sneaky peak at the new boot animation, across all devices:
CloudFlare
Kali Linux is Open Source, and Cloudflare hearts Open Source – so it’s a perfect match! As a result, CloudFlare has graciously allowed us to use their content delivery network (CDN) to mirror our repository, allowing us to now distribute our content through them. A more technical breakdown can be found on their blog.
We are currently running the CloudFlare services side by side with our standard and community mirrors.
If you notice the kali.download domain appearing on screen when you run apt update, this means you’re using CloudFlare’s services.
Kali Status
We now have a status page – status.kali.org. This provides an overview of all public facing domains and allows you to check if they are responding correctly. We have included all the sites we control, as well as the community mirrors for the repositories, allowing you to see everything you could possibly use (even if you are unaware)!
Note: Our load balancer on http.kali.org should automatically detect when a mirror is not responding and redirect you to one that is. As such, apt should always work (even if slow at times).
Metapackages
We already announced the changes to metapackages in a previous blog post, and the Kali tool listing page goes into more detail on it. However, to recap, the default toolset going forward has changed. To help with this transition, for this release only (Kali 2019.3), there is a one-off, extra image called kali-linux-large-2019.3-amd64.iso, that contains all previous default tools.
Going forward, during our release cycle, we will be evaluating which tools belong to each group:
- Kali-linux-default – tools we believe are essential to a penetration tester
- Kali-linux-large – for penetration testers who have a wider set of non standard/common situations
- Kali-linux-everything – for those who want it all (and without Internet access during the assessment)
With the switchover to GitLab (read more here), we will soon begin accepting community package submissions. This means that anyone can directly submit improvements to us–anything from minor fixes and patches to complete tool packages is encouraged. We’re currently working through the documentation on how to create a package, making it easier for folks to get started and help out. More details to come later this year.
We also noticed some packages failed to build on certain ARM architectures, which has now been fixed (allowing for more tools to be used on different platforms!).
Helper Scripts
There’s a wide range of tools in Kali. Some tools are designed to be used on Linux, some are designed for Windows (and we can still use them with WINE), and some are static resources. During our recent metapackage refresh, we took the time to create a few “helper scripts”.
You may have installed a package, gone ahead and typed in the package name to run it, and the response back was command not found. Not any more!
We understood it may not have been obvious how to use them straight away. As a result, all of our static resources should now be easy to find. Just type in the package name (Such as PayloadsAllTheThings, SecLists, WebShells and Wordlists to a name a few), you’ll see a brief description, a directory listing, and then be moved to the folder.
Tool Updates & New Packages
As always, we have our updates for all our tools, including (but not limited to):
- Burp Suite
- HostAPd-WPE
- Hyperion
- Kismet
- Nmap
There is a new tool (and it is included by default), amass, that has been well received in the bug bounty world.
GNOME Users
If you use the default Kali image, it is (currently) using GNOME for the desktop environment. If you used the command line for a period of time, chances are you noticed it was refreshing the repositories in the background. This has now been disabled.
ARM Update
For ARM devices this release, we have added support for the PINEBOOK as well as the Gateworks Ventana machines.
The RaspberryPi kernel has been bumped to version 4.19.66, which includes support for all of the RAM on 64-bit versions of the RaspberryPi 4. The RaspberryPi Zero W has seen improvements as well.
Bluetooth firmware that was accidentally dropped has been added back in, and the rc.local file has been fixed to properly stop dmesg spam from showing up on the first console.
All of the RaspberryPi images have had their /boot partition increased, which is required due to the size of the new kernel packages.
The ODROID-C2 has been bumped to the 3.16.72 for its kernel.
All images now run dpkg-reconfigure xfonts-base on their first boot – this will cause a bit of a slow down for the first boot, but the result is that if you use VNC to any of them, they will no longer show a blank screen.
On the WSL front, we have added WSL ARM64 support, which you can find in the Windows store today.
Official Kali Linux LXD Container Image Released
LXD is a next generation system container manager. It offers a user experience similar to virtual machines but using Linux containers instead.
It is image based with pre-made images available for a wide number of Linux distributions and we are excited to announce that Kali Linux is now one of them. We are working on the documentation but would like to share the excellent article from Simos Xenitellis in which he details how to install and run Kismet in a LXD Kali container.
Setup Notes
A couple of notes when installing Kali. If you choose to install Kali in a VM (rather than downloading our pre-made image), during the setup process, it should now detect if its running in VMware or VirtualBox and install the necessary packages to give you the best experience possible. However, if you have upgraded Kali rather than doing a fresh install, and never got around to installing these packages, the process has been automated by just running kali-setup. This program will have more functionally at a later date.
If you use Kali in a VirtualBox, please ensure you allocate 32 MB or more video memory to the VM, otherwise you may now run into some “interesting” issues where the screen is frozen after login through the graphical greeter, as if the computer had crashed, except that it’s working (you could confirm it by switching to another virtual terminal). If you are affected by this problem, you might see the following message from the kernel: [drm] Error -12 pinnning new fb, out of video mem?.
If you are using Kali Linux via Vagrant, the path has now changed. It can now be found here: kalilinux/rolling.
Other Downloads:
Software similar to Kali Linux 4
- 123 votesDownload the latest version of the Linux operating system.
- Freeware
- Linux
- 45 votesThe Kali Linux NetHunter project is the first Open Source Android penetration testing platform for Nexus devices, created as a joint effort between the Kali community member “BinkyBear” and Offensive Security.
- Freeware
- Android
- 35 votesArch Linux is an independently developed, i686/x86-64 general purpose GNU/Linux distribution versatile enough to suit any role.
- Freeware
- Windows
In this article and video, I will show you how to install Kali Linux 2020.1 on VirtualBox. Also, install a single boot with Kali Linux. I will cover some big changes that have been made with this new release.
“Kali Linux is an Advanced Penetration Testing Linux distribution used for Penetration Testing, Ethical Hacking and network security assessments.”
Kali Linux 2020.1 Release
On 28 January 2020, Kali has kicked off with the first release of the decade, Kali Linux 2020.1 In this article I will cover the most important changes.
Non-Root
The default credentials have been root/toor. This is no more. Kali Linux is no longer using the superuser account, root as default in Kali 2020.1. The default user account is now a standard, unprivileged, user.
root/toor is dead. Long live kali/kali
Use Kali Linux as your Main OS?
Now you can use Kali Linux as your main OS, but should you? This is up to you. There wasn’t anything really stopping you before, but Kali isn’t encouraging it. They still don’t. Therefore this is only recommended for people who are familiar with Kali enough.
Kali-Undercover
Kali Linux continues with Undercover. Kali-undercover now starts to feel even more like Windows to help blend in.
How to enable the undercover mode in Kali Linux:
Kali Single Installer Image
Kali Linux does not longer offer separate images for every desktop environment (DE). Instead, they have a single image with the option to pick your DE during installation. This means there isn’t a download link for Xfce, GNOME, KDE, MATE or LXDE DEs anymore. Just one image to rule them all.
At the install time, you may select the tools included with Kali (or none at all)! This gives you more control over what you want. Now you can install Kali without any meta-packages, giving a bare Kali installation, you can individually select what tools you want (rather than groups). More Info
Note: “Kali Live” is not included in this image. If you wish to use live mode, you’ll need the live image.
Use the space bar to check the options that you want to choose
Short keyboard explanation for “noobs” beginners ;-)
On the keyboard image below you can see the options that are used with the installation of Kali Linux.
Install Kali Linux
This step-by-step tutorial teaches you to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox.
Download Kali Linux
I would like to make another note. Personally, I always download every ISO from the original OS and certainly NO pre-made ones. Especially when it comes to Kali Linux. This is because of possible vulnerabilities.
First, you have to download the ISO file from the official Kali website. This is because, in this article and video, I choose the Kali Linux 64-Bit (Installer)
Kali Linux Download
Kali Linux Download
You can download VirtualBox here. How to download and install the VirtualBox on your Linux or Windows, I will cover that soon in a new article.
At the bottom of this article, you can watch a video of the entire Kali Linux installation.
Or click on this link to go to the video on YouTube.
Install Kali on VirtualBox
Now the download is complete, open VirtualBox and click on “New”
This will open a new screen. Give it the name “Kali Linux 2020.1” And choose the type: “Linux” and “Debian”. (Kali Linux = Debian Based). Or whatever you may use. Maybe you even use another Linux distro
After that click on “Next”
Memory size
Set at least 1 GB of RAM. “If your physical machine is 16 GB of RAM, you can set 4 GB of RAM for a virtual machine to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox.”
Personally I always set the memory size to 2 GB RAM. This is because most (when I run some tests) I have more than one Virtual Machine (VM) open.
After that click on “Next”
Hard disk
Put it on: “Create a virtual hard disk now”
And click on “Create”
Create virtual hard disk
Click on VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)
Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Storage on physical hard disk
The advantage of a dynamically allocated hard disk file is, that as the file gets larger because then it adapts to the size of the file.
“Next”
File location and size
For the install of Kali, you really need a minimal of 20 GB. In this example, I put the size to 50 GB +.
Click on “Create”
It is always good to take a generous amount of space. Better too much than too little, and you will get into trouble. Some tools or programs simply need space.
At the bottom of this article, you can watch a video of the entire Kali Linux installation.
Or click on this link to go to YouTube.
Now that the install on VirtualBox is ready so far, we are going to adjust some settings.
Click On “Settings”
Storage
Click on storage - Empty
Choose a Disk File
To select On the Disk File, click on the box that I made red next to “Optical Drive”
Then choose the Kali Linux ISO that you just downloaded.
Network
Select Network and select “Enable Network Adapter” This is usually already checked.
Select Attached to: “Bridged Adapter”. Why… There is a very simple reason for this: the default network. … Because by selecting the Bridged Adapter, your guest operating system will work on the same network as does your host. And choose wlan0
And click on “✓ OK”
There are many more options you can click and adjust. You should look for the best options for yourself.
The best thing about using a virtual environment is that you can and may make mistakes, because, you only learn from this. You just start again if it goes wrong.
Install Kali On VirtualBox
When you have adjusted all settings, it is time to install Kali Linux on your VirtualBox.
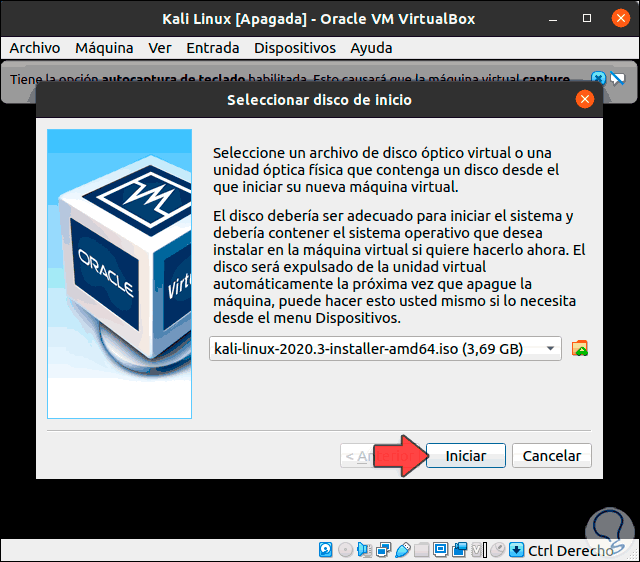
Select start-up disk
As soon as you have clicked on “Start” a new window will open. We will continue from here. Choose the correct ISO and click on “Start”
Select the correct installation
For this installation, I choose the regular “Install”, Instead of the Graphical install.
I will show both options in the Video. At the end of the video, you can see the graphical installation (in short).
Choose the lanuage for the install process
We will of course do this in English :)
Select your location
Select your location. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Kali Linux Downloads
Configure the keyboard that you will use
Depending on the Language and region, you can choose your keyboard. For this install, I choose the default American - English.
Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Choose a hostname for this system
As you can read on the screen, the hostname shows the identification from your system to your network. You can choose what you like. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Choose your domain name
I leave this open. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Setup user
Choose a user name. As you can read above, with the new Kali Linux the root user is no longer standard. Click on “enter”
“root/toor is dead. Long live kali/kali”
Usermame for the new account
Choose a password for the new user
Re-enter the password to verify
Select your time zone
Partition disk
For this Kali Linux install we use the “Use entire disk and set up encrypted LVM” So that during the start-up of Kali you are prompted for a password … “We like to be safe” Then click “enter”
Select disk to partition
Choose the correct disk that you want to use. Nothing for me to do here so “enter”
Partition scheme
Here we choose “All files in one partition, recommended for new users”. - “enter”
Write the changes to disk and configure LVM
Use the tab to jump to “Yes”.
Click on “enter”
Eresing data
Take a coffee, because this will take some time.
“The installer is now overwriting SCS12 (0,0,0), partition (sda) with random data to prevent meta-information leaks from the encrypted volume. Canceling this action, albeit at the expense of a slight reduction of the quality of the encryption”
Encryption passphrase
This took a while for this installation.
Choose a password for the encryption and click on “enter”
Re-enter the password
Amount of volume group to use for guided partitioning. In this example, I use all because this is a virtue environment. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Overview configure partitions and mount points
Write changes to disk
Use the tab to go to yes. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Install the base system
Configure the package
We don’t need an HTTP proxy, so we leave it empty. (blank). Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Choose software to Install
* Select all the options that you want to install for your Kali Linux installation
* Use the space bar to select the option. With the arrow on your keyboard for up or down.
* With this install I opted for:
* Kali desktop environment
* xfce
* Generic metapackages (kali-linux-*) I did installed the default. Enough choice for you.
✓ Standard system utilities (All the way at the bottom)
Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further. This takes some time to install. Grab yourself a coffee.
Use the space bar to check the options that you want to choose
The GRUB boot loader
Kali Linux Virtual
We certainly want to install the GRUB boot loader, so choose <Yes> Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Device for bootloader installation
Installation is complete, time to boot your system
Finally, the install of the Kali Linux install is complete. Press “enter” for a reboot.
Kali after the install
Download Kali Linux Iso For Virtualbox
Unlock disk
You have your file encrypted because of more security. Use your password to unlock the disk.
Enter your user name and password
Kali Linux Iso For Oracle Vm Virtualbox
Finally, the Kali Linux installation is successful.
A nice article to continue reading. “Best Linux Commands Hacks and other Cool Tricks for Beginners”
At the bottom of this article, you can watch a video of the entire Kali Linux installation.
Or click on this link to go to the video on YouTube.
Single Boot Kali
Installing Kali Linux on your computer is an easy process. First of all, you’ll need compatible computer hardware. Kali is supported on i386, amd64, and ARM (both armel and armhf) platforms. The hardware requirements are minimal as listed below, although better hardware will naturally provide better performance. The i386 images have a default PAE kernel, so you can run them on systems with over 4GB of RAM. Download Kali Linux and either burn the ISO to DVD or prepare a USB stick with Kali Linux Live as the installation medium. If you do not have a DVD drive or USB port on your computer, check out the Kali Linux Network Install.
Installation Prerequisites
- A minimum of 20 GB disk space for the Kali Linux install.
- RAM for i386 and amd64 architectures, minimum: 1GB, Recommended: 2GB or more.
- CD-DVD Drive / USB boot support
Kali Linux Iso Image For Virtualbox
Preparing for the Installation
- Download Kali Linux.
- Burn The Kali Linux ISO to DVD or Image Kali Linux Live to USB.
- Ensure that your computer is set to boot from CD / USB in your BIOS.
Install the ISO to USB Linux command line
Put your USB stick in your computer and give the command “fdisk -l” to “List the partition tables for the specified devices and then exit”
Make sure the USB is unmouted:
Use the command below to write your ISO to your USB
Video
In this video, I show you how to install Kali Linux on a “normal Install” Because, the install of Kali Linux is a long process, I shortened the video a bit. At 17.20 minutes in the video, the graphical install starts.
Become a member on LBRY
Plus earning LBRY for watching videos ♥️
Here an invitation link, so that we both benefit.
In this way, you also support my work.
Follow me on YouTube

Conclusion
The latest Kali Linux 2020.1 install has really surprised me because it offers an impressively rich set of tools for almost every phase of the penetration testing process, the final choice of tools to use will always depend on the tasks and goals of your current project. What for many “hackers”, pen-testers and cybersecurity engineers should be added on Kali are a number of programming options because (some) hackers like to program.
Just remember, Performing any hacks without written permission is illegal ..! Read also the Disclaimer..!
Finally
If you have any questions about this article, any feedback, suggestions if you want to share your thoughts, please feel free to do so using the below comment form.